Good credit will make it easier to achieve what you want.
This might be a new car, a new house, a credit card, or a new cell phone plan.
Most landlords, cell phone service providers, and lenders will check your credit rating before accepting your application.
Good credit will result in getting access to the best personal loans.
It will also be easier to acquire a credit card or loan with favorable terms and rates.
The FICO Score Versus the Vantage Score
In the mid – 1980s, the FICO score was generated by Fair Isaac (now called FICO).
It was created to assist lenders in working out which debtors were most likely to default.
In March 2006, the three principal credit bureaus – TransUnion, Experian, and Equifax launched the Vantage Score.
It was a new credit score created to give consistency with the scores provided by any of the three credit bureaus.
There are fundamental differences in the two credit scoring models.
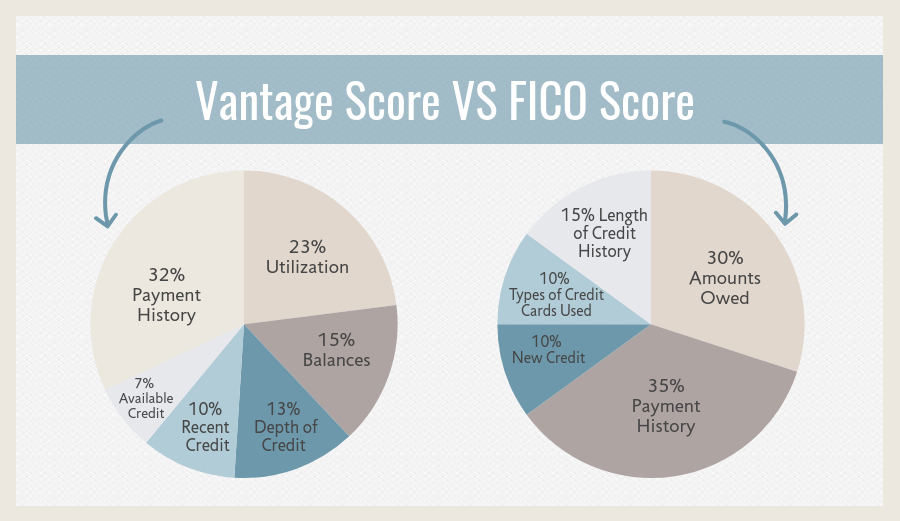
The FICO and Vantage Scores Breakdown
The FICO scoring model is the most famous score used in more than 90% of lending decisions.
The score is composed of five distinct categories of information each with a different weight attached to it:
- Payment history 35%
- Amounts owed 30%
- Length of credit history 15%
- Types of credit used 10%
- New credit 10%
Scores range from 300 to 850. The higher the score, the better.
You will never have a rating of 0, but it will take 3 to 6 months of regular activity to calculate your initial score.
The Vantage Score doesn’t have a precise breakdown, but gives this approximation:
- Hugely influential factors – payment history
- Highly influential factors – age and type of credit, the percentage of credit used
- Moderately influential factors – total debt balances
- Less influential factors – recent behavior, inquiries, and available credit
A report was published in May 5, 2015 by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).
It compared information from December 2010 with the 2010 census data.
The Bureau found that 26 million US citizens were “credit invisible.”
One in ten adults had failed to establish a credit history with a nationwide consumer reporting agency.
The report also determined that Hispanic consumers, Black consumers, and consumers in low-income neighborhoods are more liable to no credit history with an agency or not sufficient current credit history to produce a credit score.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Credit Score?
Your score is calculated when there is sufficient information on your credit report.
For FICO, you need:
- At least one account open for six months or longer.
- At least one account reported to the credit bureau within the past six months (this can be the same account that covers requirement 1).
- No report of ‘deceased’ on the credit report.
For the Vantage Score, you need an account open for one month or longer and an account published in the past two years.
How Can You Build Good Credit Quickly?
Credit cards are a very valuable credit tool. If you use them wisely they will help you build your credit.
Open a credit card account.
If you have already created some credit history, search for a card with a low spending limit.
Make small charges that you will be able to pay off straight away and pay the total balance every month.
This will allow you to establish a profile on your credit report of reliable payment and responsible credit use.
Acquire a secured credit card.
If you have a negative or minimum credit history, a secured card may be the best option.
They are connected to a savings account. The limit on the card is usually the account balance, or a percentage of the account.
If you’re having difficulty acquiring your own credit card, you can build credit by opening a joint account with someone who has a good credit history. Another alternative is becoming a certified user on someone else’s account.
You can also get a secured loan.
Some banks will offer you a passbook loan, CD loan, or credit builder loans.
These are low-risk loans intended specifically to assist you to build credit.
You deposit a specific amount into an interest bearing bank account, and borrow against that amount.
The deposit is the collateral, and interest will be paid at a higher price than interest earned by your deposit.
For passbook or CD loans, some banks will permit you to use an existing certificate of deposit or bank account as collateral.
You need to check with the lender that your on time payments will appear on your credit report.
Your Age & Your Credit Score
There is a wide disparity in credit scores by age.
Usually, the younger an individual is, the lower their credit score will be.
A credit score about 680 is considered good for a college student.
A college student would probably not need a score above 780.
A score of 640 – 680 would suffice.
However, by the time an individual is in his late forties that score is not as good when compared with others in this age bracket.
The older one gets, the easier it is to build up a diversity of credit accounts and the average age of credit.
How to Raise Your Credit Score
Scoring models use the following types of credit report information to compute your credit score.
Have you paid bills on time?
Payment history will be a considerable factor.
Your score will be adversely affected if:
- You have overdue bills
- Had an account sent to collections
- Declared bankruptcy
Are you at the maximum?
Many scoring systems compare the amount of debt you hold to your credit limits.
If the owed amount is near your credit limit, its likely to affect your score negatively.
While it is considered an advantage to have established credit accounts, too many may negatively affect your score.
Also, many scoring systems consider the kind of credit accounts you have.
How to Repair Your Credit
Apply to get the recent copies of your credit reports.
By law, you are eligible to receive a free credit report from each of the three credit bureaus each year.
Review your credit report for errors.
Read through your credit reports thoroughly and decide what needs repairing.
This could include:
- Erroneous information including payments that have been reported late, accounts that aren’t yours, etc. (You have the right to challenge any information in the report that is incomplete, inaccurate, or can’t be verified).
- Past due accounts that have been sent to collections, charged off, or are late.
- Maxed out accounts over the credit limit.
Tackle past due accounts.
Your payment history affects your credit score more than any other element.
It’s 35% of your score.
Your objective is to have all your past due accounts registered as current, or at least paid.
Bring high account balances below your limit.
Your credit utilization compares your total debt to your total credit.
It is 30% of your score.
The greater your balances are, the more it adversely affects your credit score.
Having maxed out credit cards will cost you precious points.
Your credit score reacts better to credit card balances less than 30% of the limit.
The ideal is below 10%.
To Sum It Up
We all know the advantages of having a good credit score.
And, it shouldn’t be too hard to get yourself in a favorable position.
If you’re just starting out, it will take you a month to establish an account with the Vantage Score, and 6 months in order for FICO to report your credit.
Getting started is the easy part though.
Once your credit score is established, the most important thing is to make sure you do everything you can to keep building positive credit.









Leave A Comment